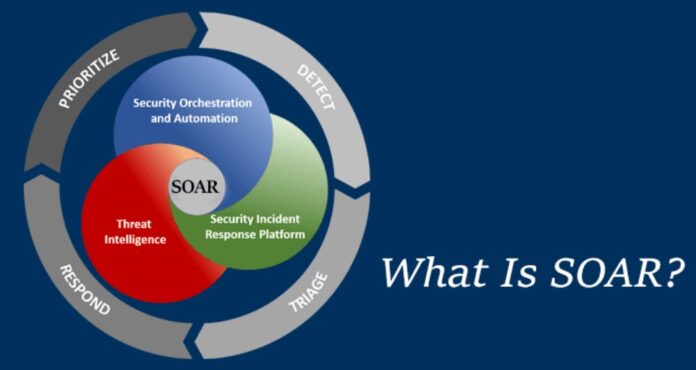
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity is a paramount concern for organizations of all sizes. With the proliferation of cyber threats, it’s crucial for businesses to adopt robust defense strategies to safeguard their sensitive data and infrastructure. One such strategy gaining prominence is Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR). This comprehensive approach combines automation, orchestration, and real-time threat intelligence to enhance incident response and mitigate security risks effectively.
Understanding the Basics of SOAR:
1. Security Orchestration:
Security orchestration refers to the coordination and management of security tools, processes, and teams to streamline incident response workflows. It involves integrating various security technologies and standardizing procedures to ensure a cohesive defense strategy. By orchestrating security measures, organizations can improve their response time and efficiency in addressing cyber threats.
2. Automation:
Automation plays a pivotal role in SOAR by reducing manual intervention in repetitive and time-consuming tasks. Through automation, routine security tasks such as threat detection, analysis, and remediation can be performed swiftly and accurately. This enables security teams to focus their efforts on more complex and high-priority issues, thereby enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
3. Response:
Effective incident response is critical in mitigating the impact of cyber attacks. SOAR platforms facilitate rapid response by providing predefined workflows and playbooks for different types of security incidents. These playbooks outline step-by-step procedures for identifying, containing, and remedying security breaches, ensuring a consistent and coordinated response across the organization.
The Advantages of SOAR:
1. Improved Efficiency:
By automating repetitive tasks and orchestrating security processes, SOAR enhances operational efficiency within cybersecurity operations. Integrating SOAR automation with AI further amplifies these benefits by enabling more sophisticated threat detection and response capabilities.This allows organizations to respond to security incidents promptly and effectively, minimizing downtime and reducing the risk of data breaches.
2. Enhanced Threat Visibility:
SOAR platforms provide comprehensive visibility into security events and incidents across the network. By aggregating data from disparate sources, such as security logs, alerts, and threat intelligence feeds, SOAR enables security teams to gain deeper insights into potential threats and vulnerabilities, empowering them to make informed decisions.
3. Scalability:
With the evolving threat landscape, scalability is essential for cybersecurity solutions. SOAR platforms are designed to scale seamlessly with the growing needs of an organization. Whether handling a small-scale security incident or a large-scale cyber attack, SOAR provides the flexibility to adapt and respond effectively to varying threat levels.
4. Consistency and Standardization:
SOAR promotes consistency and standardization in incident response processes by enforcing predefined workflows and playbooks. This ensures that security incidents are handled in a systematic and uniform manner, regardless of the personnel involved. By establishing clear guidelines, SOAR helps mitigate human errors and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Implementing SOAR in Cybersecurity:
1. Assessment and Planning:
The first step in implementing SOAR is to assess the organization’s existing security infrastructure, processes, and requirements. This involves identifying areas where automation and orchestration can add value and streamline operations. Based on the assessment, a comprehensive implementation plan should be developed, outlining goals, timelines, and resource requirements.
2. Integration of Security Tools:
SOAR platforms integrate seamlessly with existing security tools and technologies, including SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, threat intelligence feeds, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and more. Integration enables centralized management and orchestration of security operations, allowing for better coordination and collaboration among disparate security tools.
3. Creation of Playbooks:
Playbooks serve as the backbone of SOAR implementation, defining the step-by-step procedures for responding to various security incidents. Playbooks should be customized to align with the organization’s specific security policies, compliance requirements, and threat landscape. Regular testing and refinement of playbooks are essential to ensure their effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
4. Training and Skills Development:
Adequate training and skills development are crucial for maximizing the benefits of SOAR within an organization. Security teams should receive training on the use of SOAR platforms, as well as the fundamentals of automation, orchestration, and incident response. Continuous learning and skills enhancement help ensure that security personnel are equipped to leverage SOAR effectively in combating cyber threats.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) represent a paradigm shift in cybersecurity defense strategies. By integrating automation, orchestration, and real-time threat intelligence, SOAR empowers organizations to enhance their incident response capabilities and mitigate security risks effectively. With its focus on efficiency, scalability, and consistency, SOAR is poised to play a critical role in safeguarding against the evolving cyber threats of the digital age. Embracing SOAR is not just a strategic imperative but a proactive measure to stay ahead in the cybersecurity landscape.